Wireless communications
Wireless communications refers to the transmission of data or sound without the use of wires, via radio waves, microwaves, or other electromagnetic waves. This technology is used in various applications, such as mobile phones, Wi-Fi networks, Bluetooth, and GPS systems. Wireless communications provide convenience and mobility, as they allow devices to be connected over long distances without the need for physical connections. These technologies have developed the potential for fast and efficient communication on a global scale.
The Wi-Fi wireless network
Wi-Fi is a technology that allows connection to local networks without the use of cables. It uses radio waves to transmit data, allowing users to connect to networks remotely and with ease of mobility, in Wi-Fi we have two high frequencies that we broadcast 2.4Ghz and 5Ghz, in 2.4Ghz we have 13 channels (14 in Japan) and each channel is 20 MHz wide (it is possible to use a channel width of 40 MHz), in Wi-Fi 5 GHz there are 23 channels in Europe, which are available for use. These channels are 20 MHz wide, but can also be used in larger widths (40 MHz, 80 MHz, 160 MHz) for better performance.
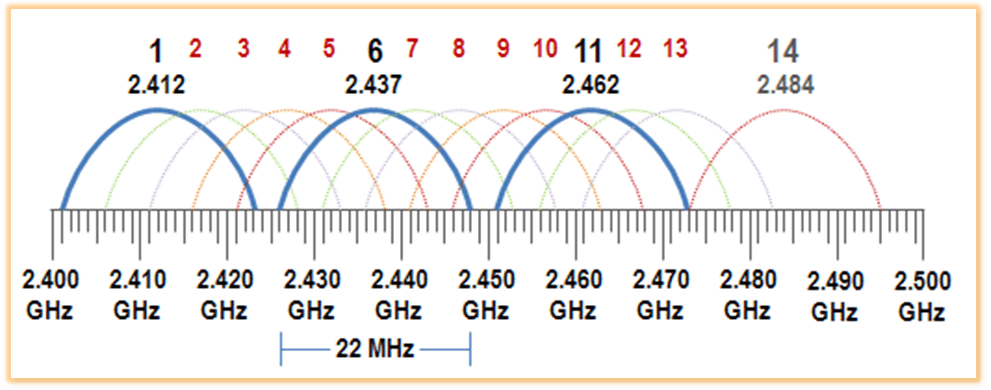
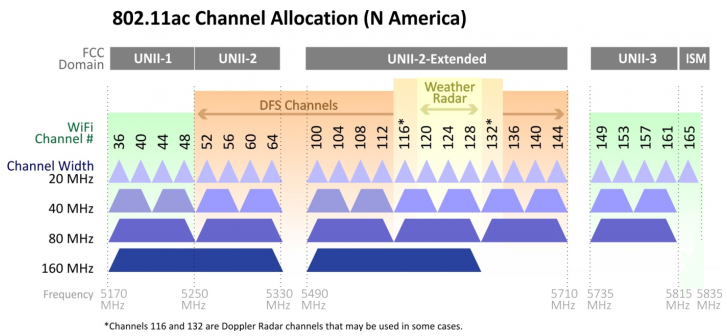
In Wi-Fi there are many technologies or "generations" that have been developed over the years such as Wi-Fi 4, 5, 6, etc., which support different speeds and frequencies.
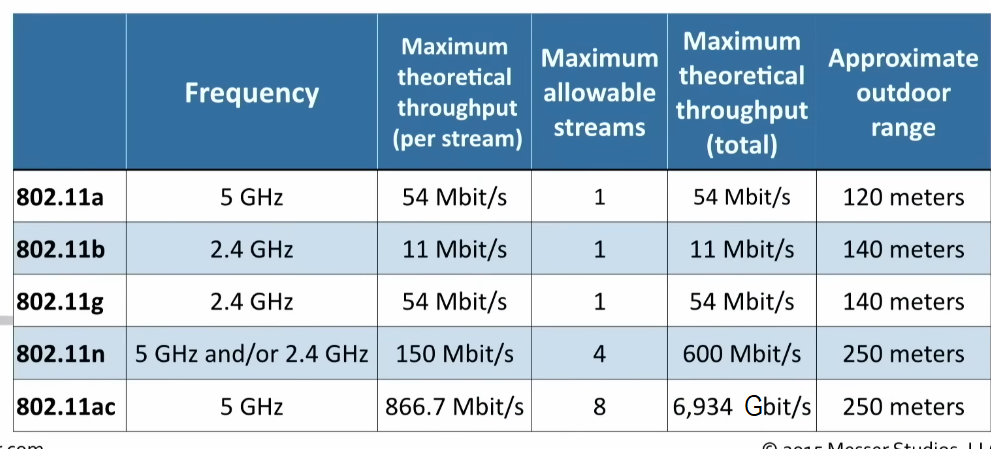
These technologies also have their technical names, for example Wi-Fi 4 is 802.11n.
Wi-Fi Security
Wi-Fi security is a crucial topic for protecting your personal data and privacy online. Wireless Wi-Fi connections are vulnerable to attacks if not properly secured. Here are some key principles for safe Wi-Fi usage:
- Strong Password: Use a strong and unique password.
- WPA2 and WPA3 Encryption: Choose WPA2 or WPA3 for the best network protection.
- Change Default Credentials: Modify the default login details of your router/access point.
- Disable WPS: Turn off Wi-Fi Protected Setup.
- Monitor Connected Devices: Check which devices are connected to your network.
- Software Updates: Regularly update the firmware of your router/access point.
- VPN or Tor: Use a VPN or Tor for additional protection on public networks.
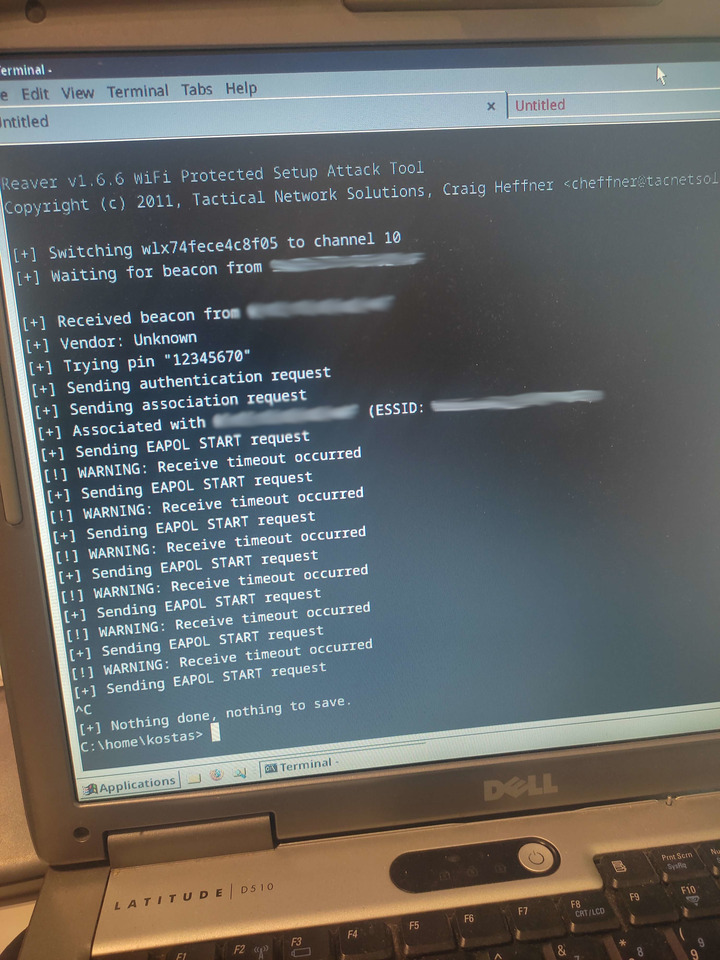
Wi-Fi is an essential tool in our daily lives, offering uninterrupted connectivity and ease of communication. Despite its advantages, it is important to be careful with the security and quality of the connection. With the right settings, Wi-Fi will continue to support our technology and communication in the best way.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a wireless communication technology that allows the exchange of data between devices over short distances, without the use of cables. It uses radio waves to connect devices such as mobile phones, computers, speakers, headphones, and others, allowing data (such as audio or files) to be sent or received without the need for a physical connection. Bluetooth has several technical characteristics and specifications that define its operation and use.
Operating Frequency
Bluetooth operates in the 2.4 GHz radio frequency (RF) range, which is the same spectrum used by other wireless technologies, such as Wi-Fi and cordless phones. This spectrum is non-directional and can cause interference between devices.
Range
The range of Bluetooth depends on the version and signal strength:
- Class 1: Up to 100 meters.
- Class 2: Up to 10 meters (the most common for consumer devices).
- Class 3: Up to 1 meter (used in special applications).
Data Transfer Speed
The data transfer speed depends on the Bluetooth version:
- Bluetooth 1.0 and 1.1: Speed up to 721 Kbps.
- Bluetooth 2.0 + EDR (Enhanced Data Rate): Up to 3 Mbps.
- Bluetooth 3.0 + HS (High Speed): Up to 24 Mbps (using Wi-Fi for higher speeds).
- Bluetooth 4.0 and later versions (4.1, 4.2, 5.0, 5.1, 5.2): Transfer speeds reach up to 50 Mbps (mainly through Bluetooth 5.0 and beyond).
Bluetooth has become an essential technology for wirelessly connecting devices, offering convenience and low power consumption. Despite the challenges, it continues to improve, making connectivity more reliable and efficient in our daily lives.
Mobile networks and 5G
Mobile networks are modern communication systems that allow the wireless transmission of data and voice between mobile devices, such as mobile phones, laptops, and other portable devices. These networks provide services such as voice communication, SMS sending, internet access, video calls, and many other applications.
Basic Operating Principles
The operation of mobile networks is based on a cellular communication technology. The coverage area of a mobile network is divided into geometric areas called cells. Each cell is covered by a cell tower and serves an area where users can make calls or connect to the internet. When the user moves from one cell to another, the network takes over the connection change (handoff) without interruption.
Network Structure and Components
A mobile network consists of various components:
- Base Stations: These antennas are located in each cell and communicate with mobile devices. Each antenna serves a specific geographic area.
- Switching Equipment: The equipment that manages calls and data. It is responsible for connecting users to the network and rerouting calls or data.
- Gateways: These units enable communication between the mobile network and other networks, such as the fixed telephone network or the internet.

Generations of Mobile Networks
Mobile networks have evolved through various generations, each bringing improvements in speed, capabilities, and coverage.
- 1G: Entirely analog communication.
- 2G (Second Generation): Introduced digital telephony and basic data services. Data transfer speeds were very low, primarily supporting voice communication and SMS. The most well-known 2G technology was GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications).
- 3G (Third Generation): Enabled broadband connectivity and faster data speeds, allowing mobile internet access, video calls, and multimedia services. The main 3G technology was UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System).
- 4G (Fourth Generation): Significantly increased internet speeds, enabling HD video streaming, real-time multimedia, and high-speed applications such as online gaming and remote work. The most popular 4G technology is LTE (Long-Term Evolution).
- 5G (Fifth Generation): Offers extremely fast data transfer speeds (up to 100 times faster than 4G), near-zero latency, and greater connectivity for multiple simultaneous devices. It enables the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and other advanced applications.
Wireless Technology and Frequencies
Mobile networks use radio frequencies to enable communication between mobile devices and base stations. These frequencies are divided into frequency bands and assigned to different types of communication (voice calls, data, SMS). The frequencies typically range from 700 MHz to 2.6 GHz and, in some cases, up to 100 GHz for 5G networks.
Types of Mobile Networks
There are different types of mobile networks, categorized based on their geographic coverage:
- Monopoly Networks: Managed by a single mobile network provider.
- Multiplexed Networks: Multiple mobile network providers operate within the same geographic area, offering services to users.
Security and Encryption
Mobile networks use advanced encryption systems to protect users' calls and data. Encryption ensures that communications remain secure and cannot be intercepted or accessed by unauthorized parties.
Interference and Network Congestion
In high-traffic areas or during peak hours, mobile networks may experience congestion, leading to slow connections or service disruptions. Mobile network providers continuously work on improving their infrastructure to prevent such issues.
It's that all ?
Mobile networks are a fundamental part of modern communication, allowing people to stay connected with each other and the internet anytime and from anywhere. With technological advancements such as 5G, new opportunities for applications and services are expected to impact our daily lives even further.